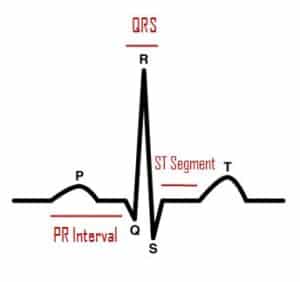
A change in the rate, origin or conduction of the cardiac electrical impulses.
Classification of Arrhythmias
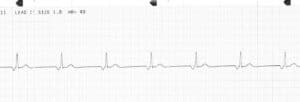
Disorders of rate
Disorders of Impulse Formation (origin)
- Atrial, Junctional, Ventricular
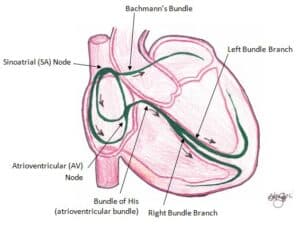
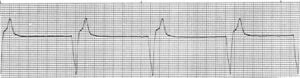
Disorders of Impulse conduction
- Conduction is blocked
- AV blocks: First Degree, Second Degree, Third Degree
- Bundle Branch Blocks